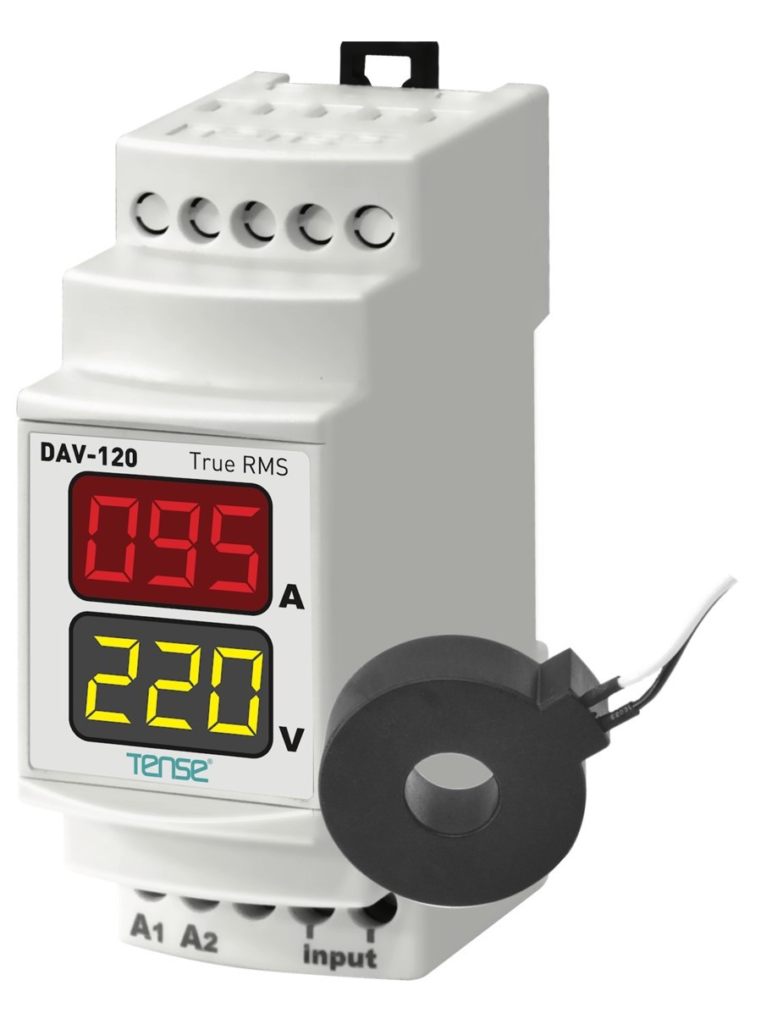
A single-phase digital ammeter and voltmeter is an essential tool for monitoring the voltage and current in electrical circuits. These meters are typically combined into one device, allowing for simultaneous measurement of both parameters. This article will guide you through the wiring process for such a device, focusing on the input phase, neutral supply, and current transformer (CT) connections.

Understanding the Terminals
A typical single-phase digital ammeter and voltmeter has four main terminals:
- A1 and A2: These terminals are for the input phase and neutral supply.
- S1 and S2: These terminals are for the current transformer (CT) connections.
Identify the Terminals:
- A1: Phase input
- A2: Neutral input
- S1: CT primary input
- S2: CT primary output

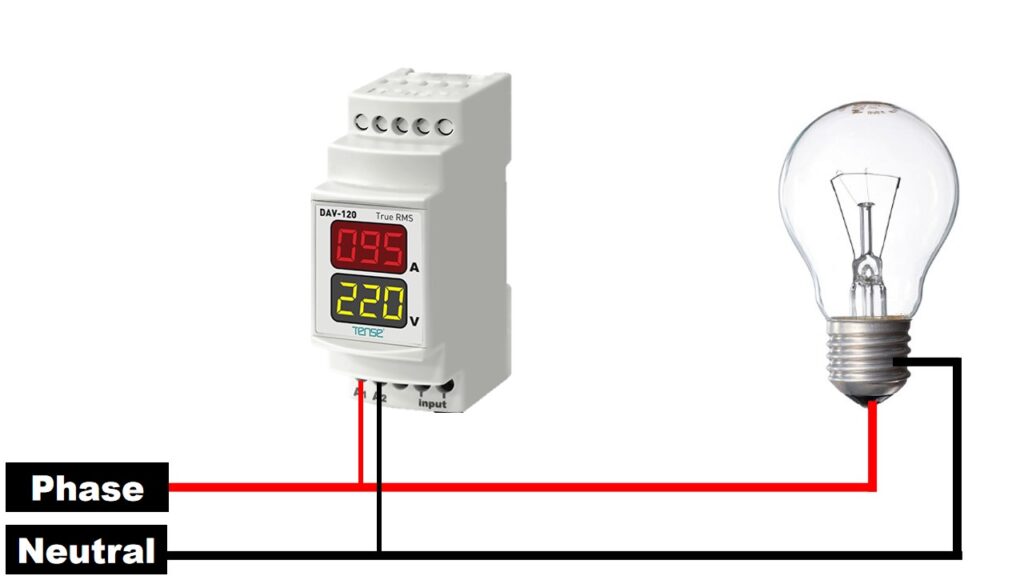
- Connecting the Input Supply:
- Connect the phase wire (live wire) from your power source to the A1 terminal.
- Connect the neutral wire from your power source to the A2 terminal.
- Installing the Current Transformer (CT):
- Place the CT around the phase wire (live wire) of the load circuit you want to measure.
- Ensure the orientation of the CT is correct as indicated by the manufacturer (typically an arrow showing the current flow direction).
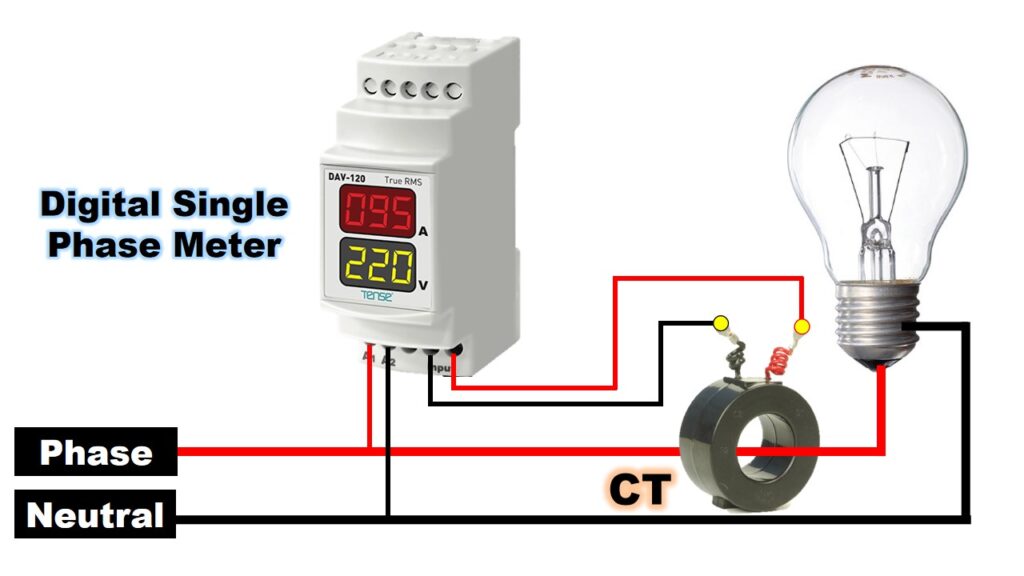
- Connecting the CT to the Meter:
- Connect one end of the CT (usually marked as S1) to the S1 terminal on the meter.
- Connect the other end of the CT (usually marked as S2) to the S2 terminal on the meter.
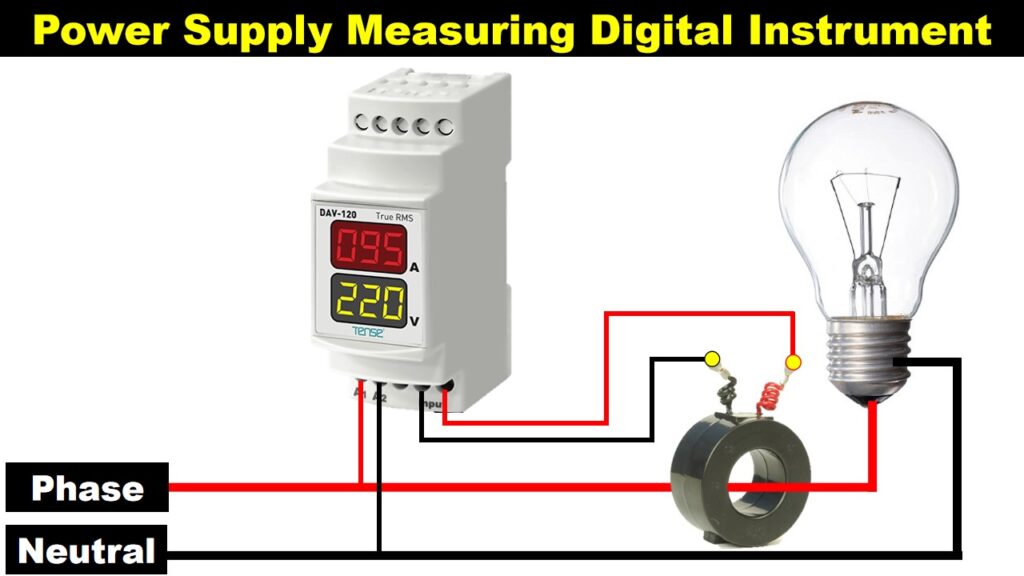
How It Works
- Voltage Measurement:
- When you connect the phase and neutral wires to A1 and A2, the meter measures the voltage between these points, displaying the voltage reading on the screen.
- Current Measurement:
- The CT senses the current flowing through the phase wire of the load. It converts this current to a smaller, proportional current that the meter can safely measure.
- The current flows from S1 through the meter to S2, allowing the meter to calculate and display the current reading.
Applications
Single-phase digital ammeters and voltmeters are widely used in residential, commercial, and industrial settings to monitor electrical parameters, ensuring the safe and efficient operation of electrical equipment. They are especially useful in applications such as:
- Home electrical panels
- Industrial machinery
- HVAC systems
- Renewable energy systems (e.g., solar power setups)

